Minimum thickness of screed
By Staenis | 14/03/2021
What is the minimum thickness of screed?
Screed, subfloor, screed... There are many names for the cement layer that forms the base for your actual floor covering. Under the screed, there is often floor insulation, with electrical and sanitary pipes underneath. But how thick does your screed need to be at a minimum? Discover the ideal screed thickness for each type of screed.
What determines the ideal thickness of a screed?
If you are going to install a floor, you must always provide a screed or chape. This cement layer forms the even and solid base for your floor covering. Are you also wondering what the minimum thickness of the chape should be? The ideal thickness of your screed depends on several factors: the type of screed, the composition of the mortar, and the presence of underfloor heating. We will go over the main types of chape and the requirements for their thickness. A flooring expert will be happy to advise you on the appropriate screed thickness and floor structure for your project. Discover your ideal floor structure here and get useful tips.
Screed thickness for bonded screed
A bonded screed is a floor screed that is laid directly on the load-bearing floor. On this load-bearing floor, a primer or bonding layer is applied beforehand to facilitate adhesion. If the cement-based screed is laid directly on the load-bearing floor, the minimum thickness of your screed is about 30 to 50 mm. If you opt for an anhydrite screed, a minimum screed thickness of 40 mm is required. Haven't arranged a screeder for your project yet? Discover how you can easily lay your own screed with the help of a handy DIY system.
The thickness of the screed for unbonded screed
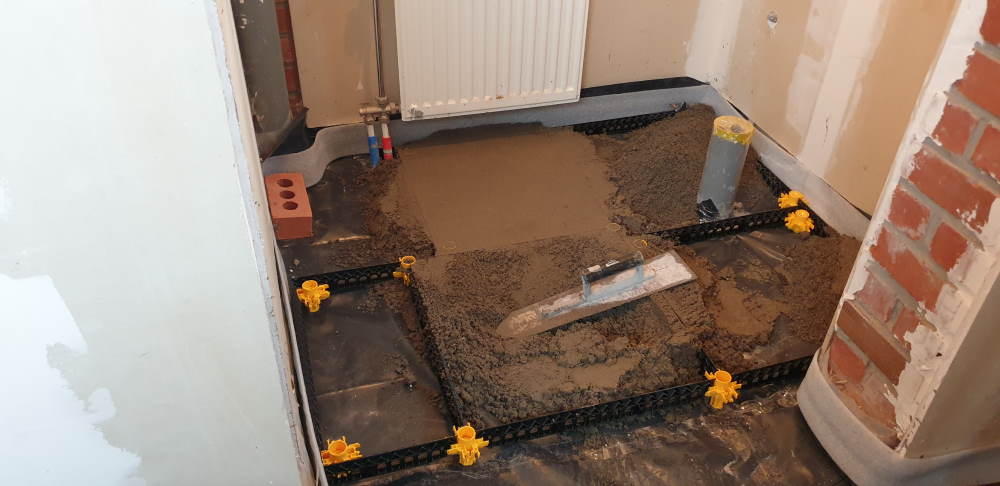
A non-bonded screed is applied on a waterproofing membrane or vapor barrier, and therefore does not come directly onto your load-bearing floor. With a regular cement-based screed, additional reinforcement with reinforcement meshes or the StaenisGrid is required. Alternatively, you can opt for a fiber-reinforced screed (fiber compound) or anhydrite screed. For cement-based screed, in this case, you should go for a minimum thickness of 50 mm. For anhydrite screed, the minimum thickness is 40 mm.
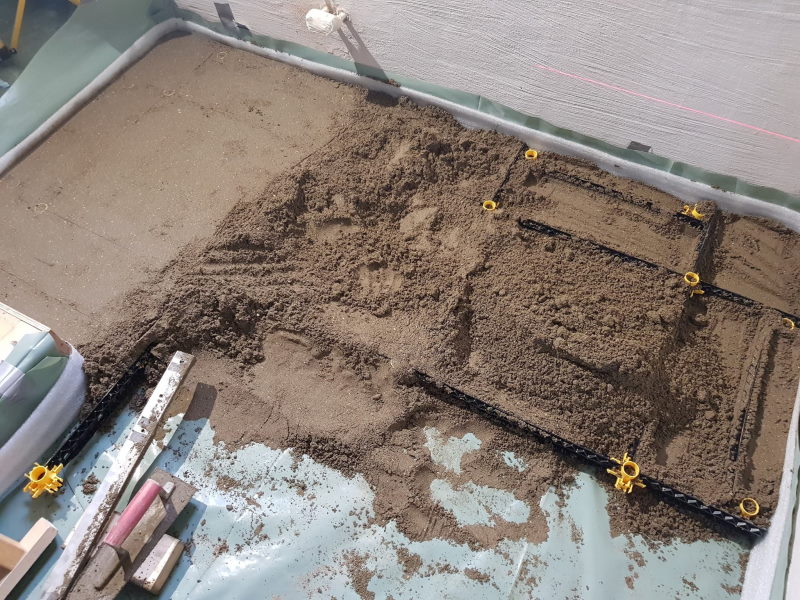

The thickness of the screed for floating screed floors
Floating screed is a screed layer that is physically separated from the underlying load-bearing floor and walls. An insulation layer is placed between the screed and the load-bearing floor and walls. This insulation layer can be installed for thermal or acoustic insulation reasons. Often, it concerns sound insulation to reduce noise nuisance in apartment buildings. Because the screed layer is detached from the load-bearing floor, additional reinforcement is always required. The minimum thickness is 50 mm for cement-based screed and 45 mm for anhydrite screed. Want to get started yourself and save significantly? With this innovative DIY system, you can easily install your own reinforced floating screed floor, even if you have no experience.
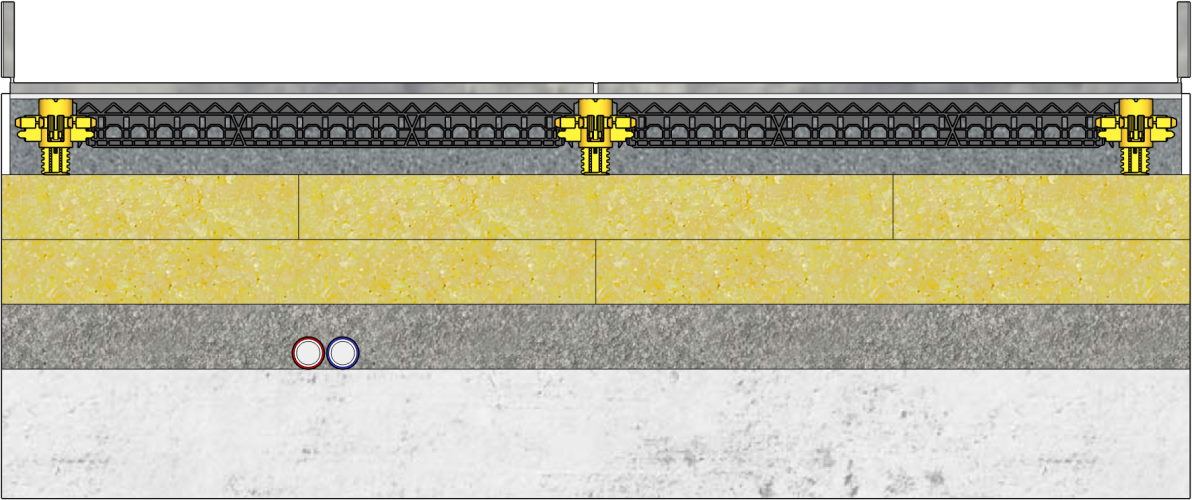
Thickness of the screed layer for anhydrite screed
Anhydrite screed is a screed based on anhydrite, a recycled gypsum. The base is therefore not cement, as with a traditional screed. Anhydrite screed is up to three times as strong as cement-bound screed. Due to its strength, the minimum thickness of anhydrite screed is slightly lower. For a bonded anhydrite screed, you can assume a thin screed with a minimum thickness of 30 mm. For an unbonded anhydrite floor, the minimum thickness is 40 mm. And for a floating anhydrite screed, the minimum thickness is 45 mm.
Screed thickness with underfloor heating
The presence of underfloor heating also affects the screed thickness. In a wet system, the underfloor heating pipes are embedded in the (wet) screed. The thickness of the screed in a wet system averages 8 centimeters. The thicker screed layer is necessary to cover the pipes, but also to better distribute the heat across the floor. Therefore, you must provide at least 45 mm of screed above the pipes. In a semi-dry system, on the other hand, the screed layer does not contain any pipes. In that case, a screed thickness of about 60 mm is sufficient for cement-based screed and a thin screed layer of about 40 mm for anhydrite screed. Want to know more about the combination of screed and underfloor heating? Be sure to read the article 'What is the minimum thickness of screed on underfloor heating?'.
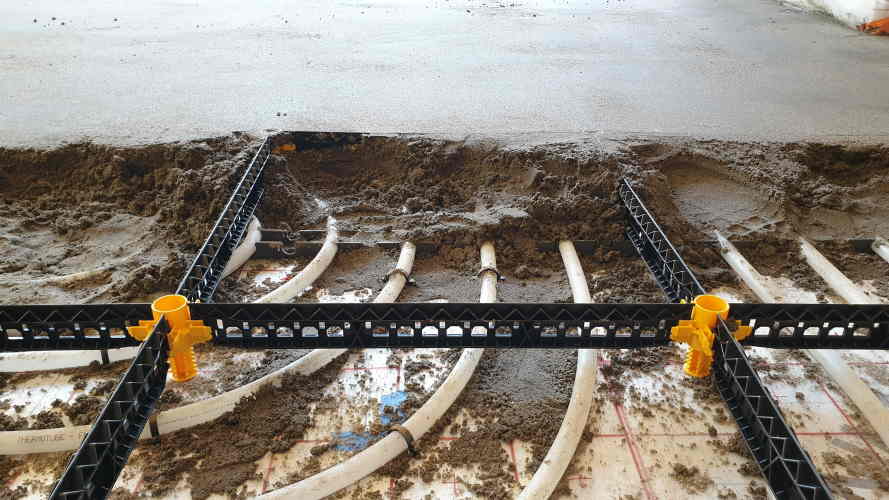

Budget tip: lay your own screed and save
Want to save on your project costs? You can do this as a DIYer by building it yourself. Laying your own screed is now possible even if you have no experience, thanks to the StaenisGrid from Staenis. This grid ensures a flat, crack-free screed floor. You save money, you don't have to wait for your screeder, and your project progresses quickly. How thick should your screed be when using the StaenisGrid? For a traditional sand-cement screed without underfloor heating, you should maintain a minimum thickness of 60 mm. For a traditional sand-cement screed with underfloor heating or in a garage, you should use an average thickness of 80 mm. [Learn here how to build your own floor structure].
Do you want to save money by installing your screed yourself? With the innovative Staenis DIY system, you can install your floor structure quickly and evenly, without the risk of cracks. Use the floor structure tool and get more information about your ideal floor structure. You can easily order your supplies online via this webshop.